 |
Data Visualization - Apache Superset Guide. Image Source: Unsplash |
Note: This article provides a comprehensive guide on deploying and using Apache Superset on a Linux server. It covers the installation and configuration process, as well as the benefits and features of Superset. While the primary focus is on Superset, we will also explore the broader concepts of business intelligence, data analytics, and visualization.
Introduction to Business Intelligence
In today's data-driven world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to gain insights and make informed decisions. This is where Business Intelligence (BI) comes into play. BI refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and presenting data to help organizations understand their performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging BI tools and techniques, businesses can unlock the power of data analytics and visualization to drive growth and gain a competitive edge.
The Role of Data Analytics in Business Intelligence
Data analytics is at the core of business intelligence. It involves the exploration, interpretation, and analysis of data to uncover meaningful patterns and insights. With the help of advanced algorithms and statistical models, businesses can extract valuable information from large datasets and gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and market trends.
Data analytics can be classified into four main types:
Descriptive Analytics: Describes what has happened in the past by summarizing historical data. It provides a snapshot of the current state and helps businesses understand trends and patterns.
Diagnostic Analytics: Focuses on identifying the causes of past events and understanding why they occurred. It helps businesses uncover the root causes behind certain outcomes or trends.
Predictive Analytics: Uses historical data and statistical models to predict future outcomes and trends. It enables businesses to make proactive decisions and anticipate potential challenges or opportunities.
Prescriptive Analytics: Goes beyond predictions and provides recommendations on the best course of action. It uses optimization techniques and simulation models to guide decision-making.
By leveraging data analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations, customer behaviour, market trends, and more. This information can then be used to drive strategic decision-making and optimize business processes.
The Power of Data Visualization in Business Intelligence
While data analytics provides the foundation for business intelligence, data visualization is the key to unlocking its true potential. Data visualization refers to the graphical representation of data, allowing users to understand complex information at a glance. By presenting data in a visual format, businesses can communicate insights effectively, spot trends, and identify patterns that might have otherwise gone unnoticed.
Data visualization offers several benefits:
Improved Data Understanding: Visualizing data makes it easier for users to grasp complex information quickly. By presenting data in a visual format, businesses can enhance data comprehension and promote better decision-making.
Enhanced Insights: Visualization helps users identify trends, patterns, and outliers in data. By visually exploring data, businesses can uncover hidden insights and make data-driven decisions.
Increased Engagement: Visual representations of data are more engaging and memorable compared to raw numbers or text. By using interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards, businesses can captivate their audience and ensure the message is conveyed effectively.
Efficient Communication: Data visualization simplifies the communication of complex ideas and findings. By presenting data visually, businesses can convey information to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner, fostering collaboration and alignment.
Apache Superset: An Introduction
Apache Superset is a modern data exploration and visualization platform that allows you to create interactive dashboards and charts with a code-free interface. It supports a wide range of data sources, including relational databases, big data platforms, and cloud-based storage solutions.
Installing Apache Superset on Linux:
Before diving into the installation process, it's essential to ensure that the required dependencies are in place. The installation process can vary depending on the operating system. Let's explore the installation steps for different environments.
Debian and Ubuntu
For Debian and Ubuntu Linux distributions, the following command installs the necessary dependencies:
sudo apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev libffi-dev python3-dev python3-pip libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev default-libmysqlclient-dev
Fedora and RHEL-derivative Linux distributions
For Fedora and RHEL-derivative Linux distributions, use the yum package manager to install the required packages:
sudo yum install gcc gcc-c++ libffi-devel python-devel python-pip python-wheel openssl-devel cyrus-sasl-devel openldap-devel
In more recent versions of CentOS and Fedora, you may need to use dnf instead of yum:
sudo dnf install gcc gcc-c++ libffi-devel python3-devel python3-pip python3-wheel openssl-devel cyrus-sasl-devel openldap-devel
On CentOS, you may also need to upgrade pip:
pip3 install --upgrade pip
Creating a Virtual Environment
pip install virtualenvvirtualenv supersetsource superset/bin/activate
Once the virtual environment is activated, all Python packages installed or uninstalled will be confined to this environment. You can exit the environment by running deactivate on the command line.
Installing Apache Superset
pip install apache-superset
After installation, the next step is to initialize the database. However, before running the database upgrade, it is important to configure the user-specified value of SECRET KEY.
Setting up Apache Superset Configuration file
Create a directory called superset or any name you prefer:
mkdir superset
Create a Python file called superset_config.py and add the file path to the PYTHONPATH environment variable.
export PYTHONPATH="${PYTHONPATH}:/visualization/superset"
To set it permanently append the above line in the shell configuration file (~/.bashrc) and reload the profile for changes to effect.
After adding this line, you can verify that the PYTHONPATH environment variable has been set correctly by running the command
echo $PYTHONPATH
Let's add the below file line to configure the SECRET KEY variable.
SECRET_KEY = 'MY_SECRET_KEY'
After SECRET KEY configuration, the next step is to initialize the database:
superset db upgrade
Once the database is initialized and the configuration is set, you can proceed to create an admin user, load example data, create default roles and permissions, and build JavaScript assets. These steps ensure a smooth installation and set up the necessary components for Superset to function properly.
Create an Admin User
To access the Superset web interface, you need to create an admin user account. You can do this by running:
superset fab create-admin
This will prompt you to enter your username, email, password, first name, and last name. You can also use any existing user account from your authentication backend by setting the AUTH_TYPE environment variable.
Load Some Sample Data
Apache Superset comes with some sample data sets that you can use to explore its features and functionalities. You can load these data sets by running:
superset load_examples
This will load some data sources and dashboards into your Superset instance. You can also add your own data sources by using the SQL Lab or the Data menu in the web interface.
Finally, to start the Superset web server, run the following command:
superset run -p 8088 --with-threads --reload --debugger
Configuring Apache Superset
Branding Apache Superset
from typing import Callable# Uncomment to setup Your App nameAPP_NAME = "Superset"# Specify the App iconAPP_ICON = "/static/assets/images/superset-logo-horiz.png"# replace the image specified in the above path or update your image name# file path: superset/lib/python3.11/site-packages/superset/static/assets/images/# replace superset with the virtual environment name# file path: venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/superset/static/assets/images/# Specify where clicking the logo would take the user# e.g. setting it to '/' would take the user to '/superset/welcome/'LOGO_TARGET_PATH = None# Specify tooltip that should appear when hovering over the App Icon/LogoLOGO_TOOLTIP = ""# Specify any text that should appear to the right of the logoLOGO_RIGHT_TEXT: Callable[[], str] | str = ""# Multiple favicons can be specified here. The "href" property# is mandatory, but "sizes," "type," and "rel" are optional.# For example:# {# "href":path/to/image.png",# "sizes": "16x16",# "type": "image/png"# "rel": "icon"# },FAVICONS = [{"href": "/static/assets/images/favicon.png"}]# replace the image specified in the above path or update your image name# file path: superset/lib/python3.11/site-packages/superset/static/assets/images/# replace superset with the virtual environment name# file path: venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/superset/static/assets/images/
Setting up MySQL or PostgreSQL as a Production Metastore
One of the requirements for installing and running Apache Superset is to have a metadata database that stores information such as user credentials, dashboard configurations, query history, and more.
By default, Superset uses SQLite as the metadata database, which is a simple and lightweight file-based database. However, SQLite has some limitations, such as a lack of concurrency support, scalability issues, and security risks. Therefore, it is recommended to use a more robust and reliable database system for production environments, such as MySQL or PostgreSQL.
To set up the production database:
pip install mysqlclient
For PostgreSQL, you need to install psycopg2:
pip install psycopg2
Create a database and a user for Superset on your database server. You can use any tool or command line interface to do this.
For example, for MySQL, you can use the following commands:
mysql -u root -pCREATE DATABASE superset;CREATE USER 'superset'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'superset';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON superset.* TO 'superset'@'localhost';
For PostgreSQL, you can use the following commands:
psql -U postgresCREATE DATABASE superset;CREATE USER superset WITH PASSWORD 'superset';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE superset TO superset;
Edit the Superset configuration file superset_config.py to specify the database URI for the metadata database.
In the configuration file, look for the line that starts with SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI and change it to point to your MySQL or PostgreSQL database.
The format of the URI is:
dialect+driver://username:password@host:port/database
For example, for MySQL, you can use:
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = 'mysql+mysqldb://superset:superset@localhost:3306/superset'
For PostgreSQL, you can use:
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = 'postgresql+psycopg2://superset:superset@localhost:5432/superset'
Initialize the metadata database by running the following command:
superset db upgrade
This will create the necessary tables and indexes for Superset in your database.
Restart Superset by running the following command
superset run -p 8088 --with-threads --reload --debugger
Email Integration
Superset can be configured to send email alerts when a SQL condition is reached and schedule reports to send screenshots of dashboards and charts.
To enable the alerts & reporting feature, update the superset_config.py file as follows:
FEATURE_FLAGS = {"ALERT_REPORTS": True,"ALERTS_ATTACH_REPORTS": True,}
Superset uses Celery Beat as a scheduler and Celery worker for sending alerts and reports.
Celery
Celery is an open-source distributed task queue framework. It allows you to run tasks asynchronously (for example sending an email) and distribute them across multiple workers. Ideal for background processing and task scheduling, etc.
Celery Beat:
Celery beat is the scheduling component of Celery, responsible for managing periodic or scheduled tasks. The schedule information can be stored in a different backend such as a database or an in-memory store.
Celery Worker:The celery worker is responsible for executing tasks that are enqueued by the Celery application. When you define and enqueue tasks in the application. It is added to a message queue (such as RabbitMQ, Redis or others) and Celery workers pull tasks from the queue and execute them. Workers are usually distributed across machines or processes, enabling you to parallelise the execution of tasks and achieve better performance and scalability.
Celery Configuration:
from celery.schedules import crontab# Celery configurationREDIS_HOST = "localhost"REDIS_PORT = "6379"class CeleryConfig:broker_url = 'redis://%s:%s/0' % (REDIS_HOST, REDIS_PORT)imports = ('superset.sql_lab', "superset.tasks", "superset.tasks.thumbnails", )result_backend = 'redis://%s:%s/0' % (REDIS_HOST, REDIS_PORT)worker_prefetch_multiplier = 10task_acks_late = Truetask_annotations = {'sql_lab.get_sql_results': {'rate_limit': '100/s',},'email_reports.send': {'rate_limit': '1/s','time_limit': 600,'soft_time_limit': 600,'ignore_result': True,},}beat_schedule = {'reports.scheduler': {'task': 'reports.scheduler','schedule': crontab(minute='*', hour='*'),},'reports.prune_log': {'task': 'reports.prune_log','schedule': crontab(minute=0, hour=0),},'email_reports.schedule_hourly': {'task': 'email_reports.schedule_hourly','schedule': crontab(minute=1, hour='*'),},}CELERY_CONFIG = CeleryConfig
SMTP Configuration:
SMTP_HOST = "smtp.mydomain.com" # change to your hostSMTP_PORT = 25 # your port, e.g. 587SMTP_STARTTLS = TrueSMTP_SSL_SERVER_AUTH = False # If your using an SMTP server with a valid certificateSMTP_SSL = FalseSMTP_USER = SMTP_USER # use the empty string "" if using an unauthenticated SMTP serverSMTP_PASSWORD = SMTP_PASSWORD # use the empty string "" if using an unauthenticated SMTP serverSMTP_MAIL_FROM = SMTP_USEREMAIL_REPORTS_SUBJECT_PREFIX = "Insights - " # optional - overwrites default value in config.py of "[Report] "# The text for call-to-action link in Alerts & Reports emailsEMAIL_REPORTS_CTA = "Explore in BI Portal"ALERT_REPORTS_NOTIFICATION_DRY_RUN = False
Screenshot Configuration:
# WebDriver configurationWEBDRIVER_TYPE = "chrome"WEBDRIVER_OPTION_ARGS = ["--force-device-scale-factor=2.0","--high-dpi-support=2.0","--headless","--disable-gpu","--disable-dev-shm-usage","--no-sandbox","--disable-setuid-sandbox","--disable-extensions",]# This is for internal use, you can keep httpWEBDRIVER_BASEURL = "http://127.0.0.1:8000"# This is the link sent to the recipient. Change to your domain, e.g. https://superset.mydomain.comWEBDRIVER_BASEURL_USER_FRIENDLY = "https://superset.mydomain.com"SCREENSHOT_LOCATE_WAIT = 100SCREENSHOT_LOAD_WAIT = 600
Generic configuration:
# Execute Alerts & Reports as admin UserTHUMBNAIL_SELENIUM_USER = 'admin'ALERT_REPORTS_EXECUTE_AS = [ExecutorType.SELENIUM]
Embedding Apache Superset Dashboards
To begin embedding Superset dashboards, follow these steps:
Enable Embedded Superset Feature:
- Edit the Feature Flag configuration by adding the Embedded Superset flag:
FEATURE_FLAGS = {"EMBEDDED_SUPERSET": True,"DASHBOARD_RBAC": True,}
- Restart the Superset instance to activate the Embedded Superset feature.
superset run -p 8088 --with-threads --reload --debugger
- Access the dashboard sub-menu and click on "Embed Dashboard."
- Enable Embedding and make a note of the generated embedding ID.
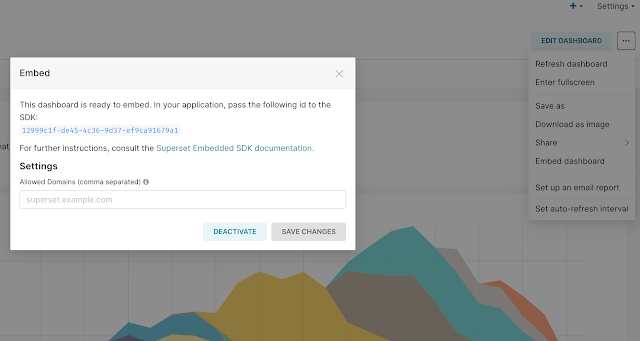 |
| Apache Superset Embedded Settings |
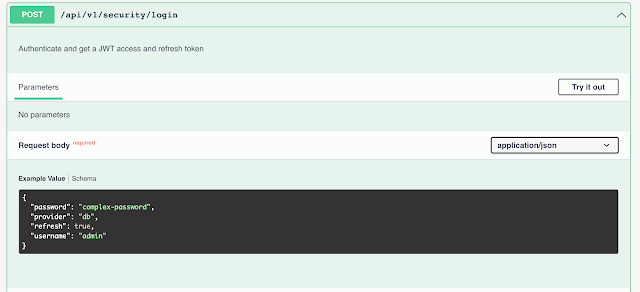 |
| Apache Superset API - Generating login token |
 |
| Apache Superset API - Generating guest token |
 |
| Apache Superset API - Swagger |
def get_login_token():url = 'https://superset.mydomain.com/api/v1/security/login'headers = {'accept': 'application/json','Content-Type': 'application/json'}data = {"password": "guestpwd","provider": "db","refresh": "true","username": "guest"}session = requests.Session()response = session.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))return response.json()
def get_guest_token(access_token):url = 'https://superset.mydomain.com/api/v1/security/login'headers = {'accept': 'application/json','Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}','Content-Type': 'application/json',}data = {"resources": [{"id": "11", "type": "dashboard"}],"rls": [],"user": {"first_name": "guest", "last_name": "user", "username": "guest"}}session = requests.Session()response = session.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))return response.json()
- Include the Superset Embedded SDK script using a CDN in the <head> section of your HTML page.
- Use the Superset Embedded SDK to embed the dashboard within an <iframe> element.
<script>async function fetchGuestTokenFromBackend() {// let response = await fetch('https://mybackend.com/fetchGuestToken', { method: 'POST'});let data = 'guest_token_value_generated_using_above_python_code'return data}supersetEmbeddedSdk.embedDashboard({id: '164104a5-69a8-484b-bb51-2a5cf7cb4a29', // given by the Superset embedding UIsupersetDomain: 'https://superset.mydomain.com',mountPoint: document.getElementById('dashboard-container'), // any html element that can contain an iframefetchGuestToken: () => fetchGuestTokenFromBackend(),dashboardUiConfig: {hideTitle:true,hideTab:true,hideChartControl:true} // dashboard UI config: hideTitle, hideTab, hideChartControls (optional)})</script>
Refer to the provided HTML and JavaScript code examples for the complete embedding process.
<html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="upgrade-insecure-requests"><title>Superset Embedded Example</title><script src="https://unpkg.com/@superset-ui/embedded-sdk"></script><link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com"><link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin><link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Noto+Sans:wght@400;700&display=swap" rel="stylesheet"><style>iframe {width: 100%;height: 100%;border: none;margin-top: 3%;}pretext {margin-right: 10%;margin-left: 10%;font-family: 'Noto Sans', sans-serif;}</style></head><body><div class="pretext"><div style=" display: flex; justify-content: center;"><h2 style="position:absolute; font-family: 'Noto Sans', sans-serif;"> [24]7 Synergen Embedded Dashboard </h2></div><div><p id="dashboard-container"></p></div><script>async function fetchGuestTokenFromBackend() {// let response = await fetch('https://mybackend.com/fetchGuestToken', { method: 'POST'});let data = 'guest_token_value_generated_using_above_python_code'return data}supersetEmbeddedSdk.embedDashboard({id: '164104a5-69a8-484b-bb51-2a5cf7cb4a29', // given by the Superset embedding UIsupersetDomain: 'https://superset.mydomain.com',mountPoint: document.getElementById('dashboard-container'), // any html element that can contain an iframefetchGuestToken: () => fetchGuestTokenFromBackend(),dashboardUiConfig: {hideTitle:true,hideTab:true,hideChartControl:true} // dashboard UI config: hideTitle, hideTab, hideChartControls (optional)})</script></div></body></html>
You can refer the superset embedded sdk document for other configuration details.
SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True # Prevent cookie from being read by frontend JS?FEATURE_FLAGS = {"EMBEDDED_SUPERSET": True,"DASHBOARD_RBAC": True,"ENABLE_TEMPLATE_PROCESSING": True,"MENU_HIDE_USER_INFO": False,"DRILL_TO_DETAIL": True,"DASHBOARD_CROSS_FILTERS": True}SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE = True # Prevent cookie from being transmitted over non-tls?SESSION_COOKIE_SAMESITE = "None" # One of [None, 'None', 'Lax', 'Strict']SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN = False# Cross-OriginENABLE_CORS = TrueCORS_OPTIONS = {'supports_credentials': True,'allow_headers': ['*'],'resources':['*'],'origins': ['*', 'http://127.0.0.1:5500'],}# Dashboard embeddingGUEST_ROLE_NAME = "Gamma"GUEST_TOKEN_JWT_SECRET = "your_secret_key"GUEST_TOKEN_JWT_ALGO = "HS256"GUEST_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME = "X-GuestToken"GUEST_TOKEN_JWT_EXP_SECONDS = 3600 # 60 minutes
By following the outlined steps and utilizing the Superset Embedded SDK, you can seamlessly integrate Superset dashboards into your external applications. This empowers users with enhanced data visualization capabilities and enables efficient analysis within a unified environment. The combination of Superset's embedding feature and its robust data visualization capabilities makes it an invaluable tool for data-driven applications
Apache Superset Authentication: Implementing OAuth2 with Azure Identity Platform
Flask App Builder offers a range of authentication methods to bolster security within your applications. These include:
- Database
- OpenID
- LDAP
- Remote User
- OAuth
We will explore the process of implementing OAuth2 authentication using the Azure Identity Platform for Apache Superset.
Azure AD OAuth2 Authentication Implementation
Assuming you have registered your application in Azure AD and generated the required client secret for configuration purposes, follow these steps:
Register your application in Azure AD and make note of the Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret. If not done already, refer to the documentation on registering a client application with the Microsoft Identity Platform.
Implement OAuth2 authentication for your Apache Superset instance:
Edit your Apache Superset configuration file (superset_config.py) and add the following configurations:
from flask_appbuilder.security.manager import AUTH_OAUTH# Set the authentication type to OAuthAUTH_TYPE = AUTH_OAUTH# Self registration & default roleAUTH_USER_REGISTRATION = TrueAUTH_USER_REGISTRATION_ROLE = "Admin"OAUTH_PROVIDERS = [{"name": "azure","icon": "fa-windows","token_key": "access_token","remote_app": {"client_id": "your client id","client_secret": "your client secret","api_base_url": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/tenant_id/oauth2","client_kwargs": {"scope": "User.read name preferred_username email profile upn groups","resource": "your client id",},"request_token_url": None,"access_token_url": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/tenant_id/oauth2/token","authorize_url": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/tenant_id/oauth2/authorize",},},]
Create a custom Security Manager class that extends the Superset Security Manager class with the following settings:
import loggingfrom superset.security import SupersetSecurityManagerclass CustomSsoSecurityManager(SupersetSecurityManager):def _get_oauth_user_info(self, provider, resp=None):#logging.debug("Oauth2 provider: {0}.".format(provider))if provider == "azure":#logging.debug("Azure response received : {0}".format(resp))id_token = resp["id_token"]#logging.debug(str(id_token))me = self._azure_jwt_token_parse(id_token)#logging.debug("Parse JWT token : {0}".format(me))return {"name": me.get("name", ""),"email": me["upn"],"first_name": me.get("given_name", ""),"last_name": me.get("family_name", ""),"id": me["oid"],"username": me["oid"],"role_keys": me.get("roles", []),}oauth_user_info = _get_oauth_user_info
Save this file as custom_sso_security_manager.py and import the Custom Security Manager in your configuration file:
from custom_sso_security_manager import CustomSsoSecurityManagerCUSTOM_SECURITY_MANAGER = CustomSsoSecurityManager
Update your client application's redirect URL:
https://superset.mydomain.com/oauth-authorized/azure
After restarting, you will notice the updated login page reflecting your changes.
Azure AD:
 |
| Apache Superset OAuth2- Azure AD Authentication |
If you have configured multiple Identity Providers, you can see multiple providers option in sign-in page:
 |
| Apache Superset OAuth2 Authentication |
By following these steps, you can successfully implement OAuth2 authentication with the Azure Identity Platform for your Apache Superset instance. This integration ensures a secure authentication process while enabling seamless user access to the platform.
Benefits and Features of Apache Superset
User-Friendly Interface: Superset provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface that makes it easy for users to explore and analyse data. With drag-and-drop functionality and interactive visualisations, users can create insightful dashboards without writing complex queries or code.Wide Range of Data Sources: Superset supports a variety of data sources, including popular databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite, as well as big data platforms like Apache Hive, Apache Spark, and Presto. It also integrates with cloud-based storage solutions like Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage.Interactive Dashboards: Superset allows users to create interactive dashboards with a wide range of visualization options, including charts, graphs, maps, and tables. Users can customize the appearance and layout of dashboards and easily share them with others.Ad-Hoc Analysis: With Superset, users can perform ad-hoc analysis by exploring and filtering data in real-time. The SQL Lab feature allows users to write and execute SQL queries directly in the browser, providing instant results and insights.Collaboration and Sharing: Superset enables collaboration by allowing users to share dashboards, charts, and SQL queries with others. Users can set permissions and access controls to ensure data security and privacy.Extensibility and Customization: Superset is highly extensible and customizable, allowing users to add custom visualizations, plugins, and integrations. The Superset community actively contributes to the development of new features and enhancements.Scalability and Performance: Superset is designed to scale out in distributed environments and can handle large datasets and high user concurrency. It leverages technologies like Apache Druid and Apache Arrow to provide fast and efficient data processing.Active Community Support: Apache Superset has a vibrant and active community of users and contributors. The community provides support, documentation, and regular updates, ensuring that Superset remains a robust and reliable tool for business intelligence.

0 thoughts:
Post a Comment